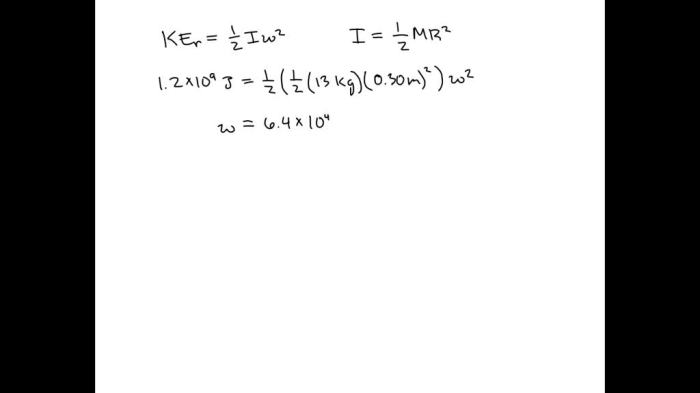A flywheel is a solid disk that rotates – A flywheel, a solid disk that rotates, is a mechanical device that plays a pivotal role in energy storage and application. Its ability to store kinetic energy and release it smoothly makes it a valuable asset in various industries. This article delves into the concept, design, and applications of flywheels, exploring their unique characteristics and potential in shaping future technologies.
Flywheels have a cylindrical shape with a solid, heavy rim and a relatively thin hub. They are typically made of high-strength materials like steel or composite materials to withstand the high centrifugal forces generated during rotation. The weight distribution and balance of the flywheel are crucial for ensuring stability and minimizing vibrations.
1. Concept and Definition: A Flywheel Is A Solid Disk That Rotates
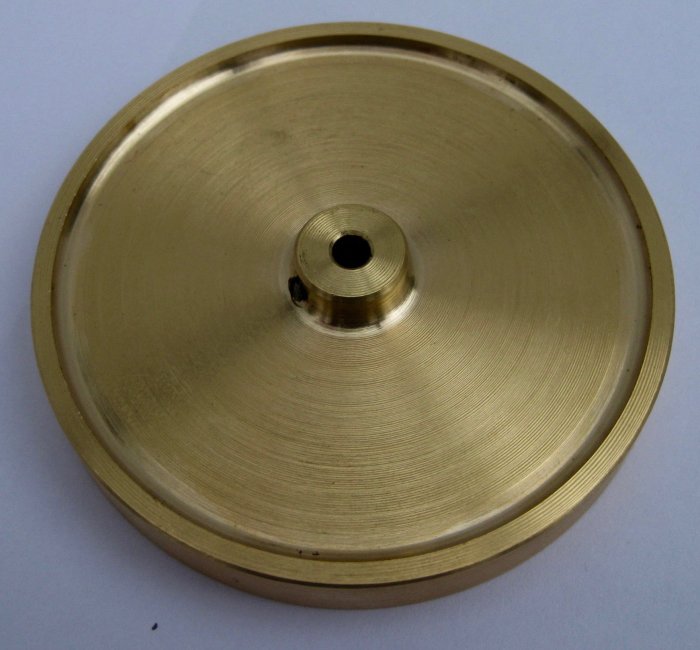

A flywheel is a solid disk or cylinder that rotates around an axis, primarily designed to store rotational energy. Flywheels serve as a mechanical energy reservoir, releasing and absorbing energy through changes in their rotational speed.
Physical Characteristics
Flywheels typically have a disk or cylindrical shape, with dimensions varying based on the application. They are constructed using materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. Weight distribution and balance are crucial in flywheel design to minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation.
Principles of Operation
Flywheels operate based on the principle of rotational inertia, which resists changes in their rotational motion. As the flywheel rotates, it stores kinetic energy in proportion to its mass and the square of its angular velocity. Energy is transferred into the flywheel by applying an external torque, which increases its speed, and extracted by applying a resistive torque, which decreases its speed.
Applications
- Energy storage systems:Flywheels are used in renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and solar arrays, to store excess energy and release it during periods of high demand.
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS):Flywheels provide backup power in the event of power outages, ensuring a continuous supply of electricity to critical systems.
- Transportation:Flywheels are being explored for use in electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles to improve fuel efficiency and extend driving range.
Design and Optimization, A flywheel is a solid disk that rotates
Flywheel design involves optimizing factors such as size, weight, and speed for specific applications. Materials, weight distribution, and balancing techniques play a significant role in achieving optimal performance. Trade-offs between factors, such as energy storage capacity and cost, must be carefully considered.
Future Developments
Ongoing research in flywheel technology focuses on improving energy density, reducing costs, and exploring novel applications. Flywheels are being investigated for use in spacecraft propulsion systems, renewable energy storage, and as energy buffers in power grids.
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of a flywheel?
The primary function of a flywheel is to store kinetic energy and release it smoothly, providing a stable power source or absorbing fluctuations in energy demand.
How does a flywheel store energy?
A flywheel stores energy in the form of rotational kinetic energy. As the flywheel rotates, its angular velocity increases, and so does its stored energy.
What are the advantages of using flywheels?
Flywheels offer several advantages, including high energy density, fast response time, long lifespan, and low maintenance requirements.