Embark on a scientific odyssey with our comprehensive gel electrophoresis worksheet answer key, a beacon of knowledge that illuminates the intricate world of DNA analysis. This definitive guide empowers you to master the principles, procedures, and applications of gel electrophoresis, unlocking the mysteries of molecular biology.
Delve into the intricacies of gel electrophoresis, unraveling the principles that govern the separation of DNA fragments. Understand the crucial role of agarose gel and electrophoresis buffer, and explore the factors that influence DNA migration during electrophoresis. Immerse yourself in a step-by-step protocol that demystifies the gel electrophoresis procedure, guiding you through the preparation of the gel, loading of DNA samples, and execution of electrophoresis.
1. Gel Electrophoresis Theory
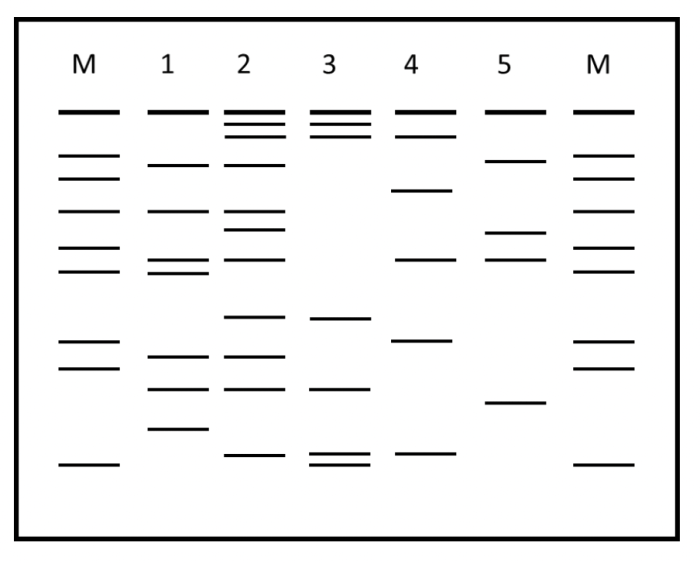
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory technique used to separate DNA fragments based on their size and electrical charge. It is a fundamental technique in molecular biology and has a wide range of applications in research and diagnostics.
Principles of Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis involves placing DNA samples in an agarose gel, which is a porous matrix made from seaweed extract. The gel is submerged in an electrophoresis buffer, which contains ions that create an electrical field. When an electrical current is applied to the gel, the negatively charged DNA fragments migrate towards the positive electrode.
Role of Agarose Gel and Electrophoresis Buffer, Gel electrophoresis worksheet answer key
The agarose gel acts as a molecular sieve, with smaller DNA fragments moving through the pores more easily than larger fragments. The electrophoresis buffer provides the ions necessary for the electrical field and helps to maintain a consistent pH during electrophoresis.
Factors Affecting DNA Migration During Electrophoresis
The migration of DNA fragments during electrophoresis is affected by several factors, including:
- Size of DNA fragments: Smaller fragments migrate faster than larger fragments.
- Agarose gel concentration: A higher gel concentration results in slower migration.
- Electrophoresis buffer composition: Different buffers can affect the migration rate of DNA fragments.
- Voltage applied: A higher voltage results in faster migration.
Helpful Answers: Gel Electrophoresis Worksheet Answer Key
What is the purpose of gel electrophoresis?
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory technique used to separate DNA fragments based on their size and charge.
How does gel electrophoresis work?
DNA fragments are placed in an agarose gel and subjected to an electrical current. The negatively charged DNA fragments migrate towards the positive electrode, with smaller fragments moving faster than larger ones.
What are the applications of gel electrophoresis?
Gel electrophoresis is used in a variety of molecular biology applications, including DNA analysis, gene cloning, and forensic science.