Noble gas used in some lasers – Noble gases, with their unique properties, have found a home in the realm of lasers, enabling these devices to emit coherent beams of light that have revolutionized various fields. Their presence in lasers grants these systems exceptional performance, making them indispensable tools in science, medicine, and technology.
From understanding the atomic structure of noble gases to exploring their applications in lasers, this comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of noble gases and their role in shaping the laser industry.
Noble Gas Properties
Noble gases are a group of elements that share unique properties that make them ideal for use in lasers. These properties include low reactivity, high ionization energy, and the ability to emit light at specific wavelengths.
The noble gases commonly used in lasers include helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), and xenon (Xe). These gases are all monatomic, meaning they exist as single atoms rather than molecules. This makes them highly stable and resistant to chemical reactions.
Atomic Structure and Laser Applications
The atomic structure of noble gases plays a key role in their use in lasers. The electrons in noble gas atoms are arranged in a stable configuration, with all of the energy levels filled. This makes them less likely to absorb or emit light, which is essential for laser operation.
When a noble gas atom is excited by an electrical current or other energy source, the electrons can move to higher energy levels. When the electrons return to their original energy levels, they emit light at a specific wavelength. The wavelength of the light depends on the energy difference between the two energy levels.
Laser Applications
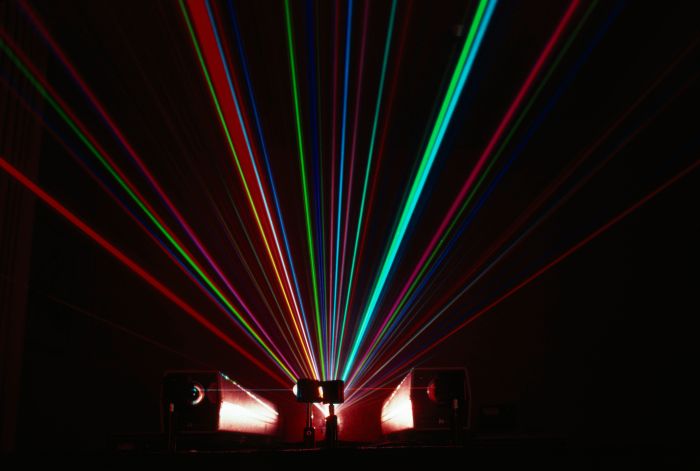

Noble gases, with their unique properties, play a crucial role in the development and operation of various types of lasers.
One notable application is the helium-neon (HeNe) laser, which utilizes a mixture of helium and neon gases. The energy levels of helium and neon atoms allow for the production of a highly stable and monochromatic red laser beam. HeNe lasers are commonly used in applications such as barcode scanners, laser pointers, and optical alignment systems.
Argon-ion Lasers
- Argon-ion lasers utilize ionized argon gas as the lasing medium.
- They emit blue-green laser light with high power and coherence.
- Applications include medical procedures, laser cutting, and scientific research.
Krypton-ion Lasers
- Krypton-ion lasers employ ionized krypton gas for laser emission.
- They produce blue, green, and red laser lines with moderate power and coherence.
- Applications include laser engraving, laser marking, and medical treatments.
Excimer Lasers
- Excimer lasers use noble gases combined with reactive gases to generate ultraviolet laser light.
- They produce short, high-energy pulses of light, making them suitable for applications such as micromachining, laser surgery, and semiconductor fabrication.
Laser Design and Construction

Lasers utilizing noble gases are meticulously engineered, taking into account specific design considerations to achieve optimal performance and efficiency. These considerations include the choice of noble gas, the configuration of the laser cavity, and the methods employed to introduce and maintain the noble gas within the system.
Noble Gas Selection
The selection of the noble gas used in a laser is crucial and depends on the desired laser properties, such as wavelength, power, and stability. Different noble gases exhibit unique characteristics that influence these parameters. For instance, helium-neon lasers are renowned for their stability and long lifespan, while argon-ion lasers offer high power and a wider wavelength range.
Lasers rely on noble gases, such as helium and argon, for their operation. These gases emit light when stimulated, making them ideal for various applications. Incidentally, if you’re seeking guidance on financial management, Dave Ramsey’s Chapter 6 answers offer practical advice on budgeting and debt repayment.
Returning to the topic of lasers, the noble gases employed in their construction contribute significantly to their efficiency and precision.
Laser Cavity and Optical Resonator
The laser cavity, also known as the optical resonator, is the heart of the laser system. It consists of two mirrors positioned at opposite ends of a gas-filled tube. The mirrors reflect the laser light back and forth, creating a resonant cavity that amplifies the light through stimulated emission.
The noble gas is contained within this cavity, where it interacts with the laser light.
Noble Gas Introduction and Maintenance
Introducing and maintaining the noble gas in the laser system is essential for its proper operation. The gas is typically introduced into the cavity through a vacuum system, which removes any impurities or contaminants. To maintain the gas pressure and purity, the laser system may incorporate getters or other purification techniques.
Additionally, the gas may be recirculated or replenished over time to ensure optimal performance.
Laser Safety: Noble Gas Used In Some Lasers

The use of noble gases in lasers requires careful attention to safety considerations to minimize potential hazards and ensure responsible operation.
Noble gases are inert and non-toxic, but when used in high-power lasers, they can present several risks:
- Electrical hazards:High voltages and currents are used to excite the noble gas atoms, creating the laser beam. Improper handling can lead to electrical shock or electrocution.
- Fire hazards:The intense heat generated by the laser beam can ignite flammable materials in the vicinity of the laser.
- Eye hazards:The laser beam can cause severe eye damage if it directly strikes the eyes. Direct or indirect exposure to the beam, even at low power levels, can lead to retinal burns and vision impairment.
- Skin hazards:Prolonged exposure to the laser beam can cause skin burns and irritation.
To ensure safety, strict protocols and regulations are in place for handling and operating noble gas lasers:
Safety Measures and Protocols
- Laser safety training:All personnel involved in operating noble gas lasers must receive comprehensive training on laser safety hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures.
- Laser safety eyewear:Appropriate laser safety eyewear that meets the required optical density (OD) rating must be worn at all times when working with noble gas lasers.
- Laser safety enclosures:Lasers must be enclosed in properly designed safety enclosures that prevent accidental exposure to the laser beam.
- Interlocks and warning systems:Interlocks and warning systems should be implemented to prevent unauthorized access to the laser area and alert personnel to potential hazards.
- Emergency procedures:Clear emergency procedures must be established and communicated to all personnel in case of accidents or malfunctions.
Regulations and Standards, Noble gas used in some lasers
The use of noble gases in lasers is governed by regulations and standards set by national and international organizations, such as:
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI):ANSI Z136 series of standards provide guidelines for laser safety, including safe use of noble gas lasers.
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC):IEC 60825 series of standards provide international guidelines for laser safety.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA):OSHA regulations in the United States cover laser safety, including the use of noble gas lasers.
Adhering to these regulations and standards is crucial to ensure the safe operation of noble gas lasers and minimize potential hazards.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the advantages of using noble gases in lasers?
Noble gases offer several advantages, including low reactivity, high energy levels, and the ability to produce specific wavelengths of light, making them ideal for various laser applications.
What are some common types of lasers that utilize noble gases?
Helium-neon lasers, argon-ion lasers, and krypton-ion lasers are among the most common types of lasers that employ noble gases as the active medium.
What safety precautions should be taken when working with noble gas lasers?
Proper handling and operation of noble gas lasers require adherence to safety measures such as wearing protective eyewear, ensuring adequate ventilation, and following established protocols for laser operation.
